Over the past couple of months, you’ve consistently sold 400 units, meaning you’re exceeding your goal and generating profit. On the other hand, if you’re only selling 250 units, you’ll need to either increase sales or lower costs to hit that target. Tracking this data over time can help you identify patterns — e.g., slower sales during specific months — so you can adjust your strategy based on those trends. Break-even analysis looks at internal costs and revenues, but doesn’t factor in external influences that can impact your business. — e.g., changes in market demand, economic conditions, inflation, supply chain disruptions, etc. For instance, if shipping costs rise due to global supply chain problems, your variable costs might go up and can throw off your original calculation.
- This margin indicates how much of each unit’s sales revenue contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit once fixed costs are met.
- For example, semi-variable costs, which have both fixed and variable components, can complicate the accuracy of the breakeven calculation which then changes the breakeven point in units.
- A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.
Sports & Health Calculators
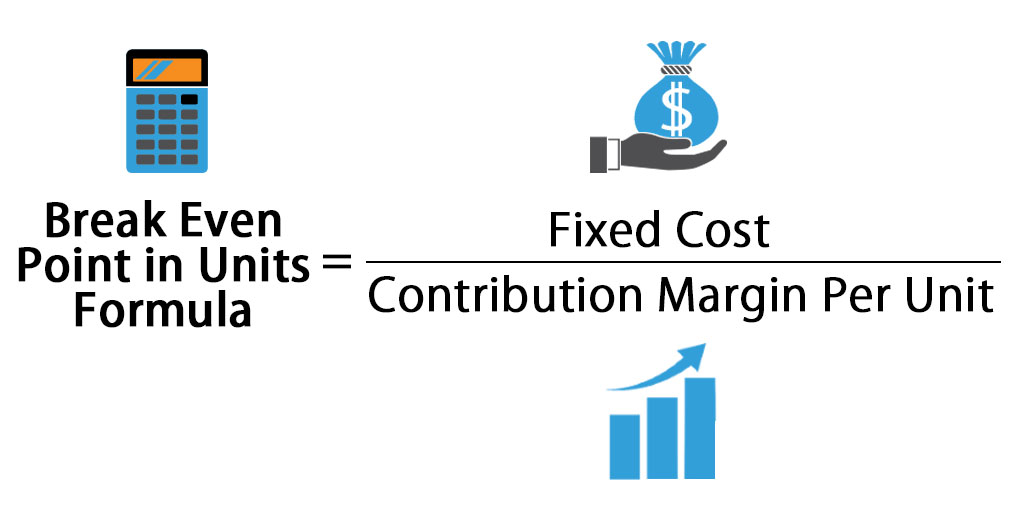
In this breakeven point example, the company must generate $2.7 million in revenue to cover its fixed and variable costs. The breakeven formula for a business provides a dollar figure that is needed to break even. This can be converted into units by calculating the contribution margin (unit sale price less variable costs). Dividing the fixed costs by the contribution margin will reveal how many units are needed to break even.
Using break-even analysis to determine level of production

Variable costs are incurred only when a sale is made, meaning you only pay for what you need. Outsourcing these nonessential costs will lower your profit margin and require you to sell fewer products to make a profit. Launching a new product or service can be exciting but equally intimidating, especially when you’re unsure how much you’ll need to sell to cover your costs. It helps you figure out how many units you need to sell or services you need to provide to make sure your investment pays off.
Get Started
Say your variable costs decrease to $10 per unit, and your fixed costs and sales price per unit stay the same. In our example above, Maria’s break-even point tells her she needs to create eight quilts a month, right? But what if she knows she can create only six a month given her current time and resources? Well, per the equation, she might need to up her cost per unit to offset the decreased production.
Importance of Break-Even Point Analysis
These costs can add to your overall expenses, pushing your break-even point further out. This means the startup would need to sell 750 subscriptions each month to break even. Once the startup exceeds this number, every additional subscription sold contributes straight to profit. For example, suppose a startup offers what is the difference between sales tax and vat a subscription-based software for project management and they want to know how many subscriptions they need to sell. The break-even point (BEP) is where the total money coming into your business (revenue) matches what’s leaving (expenses). It’s all about understanding when your sales will finally cover total costs.
How do you calculate your break-even point?
For example, if you raise the price of a product, you’d have to sell fewer items, but it might be harder to attract buyers. You can lower the price, but would then need to sell more of a product to break even. It can also hint at whether it’s worth using less expensive materials to keep the cost down, or taking out a longer-term business loan to decrease monthly fixed costs. A break-even analysis helps business owners find the point at which their total costs and total revenue are equal, also known as the break-even point in accounting.
In accounting terms, it refers to the production level at which total production revenue equals total production costs. In investing, the breakeven point is the point at which the original cost equals the market price. Meanwhile, the breakeven point in options trading occurs when the market price of an underlying asset reaches the level at which a buyer will not incur a loss. When you outsource fixed costs, these costs are turned into variable costs.
Note that in this formula, fixed costs are stated as a total of all overhead for the firm, whereas price and variable costs are stated as per unit costs—the price for each product unit sold. The Break Even Revenue Calculator is a vital tool for understanding how much revenue you need to generate in order to cover your operating expenses. By using the formula to calculate your break-even revenue, you can make informed decisions about pricing, cost-cutting measures, and sales targets.
